Is sugar addictive? This question sparks heated debates among nutritionists and health professionals alike. While traditional addictive substances such as alcohol and nicotine have strict clinical classifications, sugar has increasingly been linked to cravings for sugar and compulsive eating behaviors. With the alarming rise in sugar consumption, especially in the form of added sugar in processed foods, individuals often find themselves grappling with the health effects of sugar on their bodies. Understanding the nuances of sugar addiction is crucial as we navigate our sweet choices in today’s ultra-processed food landscape.
The discussion surrounding the potential addiction to sweeteners, commonly known as sugar dependency, raises significant interest in health circles. Some studies suggest that certain food substances can lead to increased cravings, similar to what is observed with more traditionally recognized addictive substances. Additionally, nutrition experts emphasize the psychology behind sugar consumption, making it imperative to consider the role of sugary foods in our diets. While many enjoy the enjoyable rush of sweetness, it is vital to distinguish between healthy sugar intake and overindulging in sugary snacks that can seriously impact one’s health. The ongoing exploration of how added sugars influence our eating habits sheds light on a larger conversation about dietary choices in modern society.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
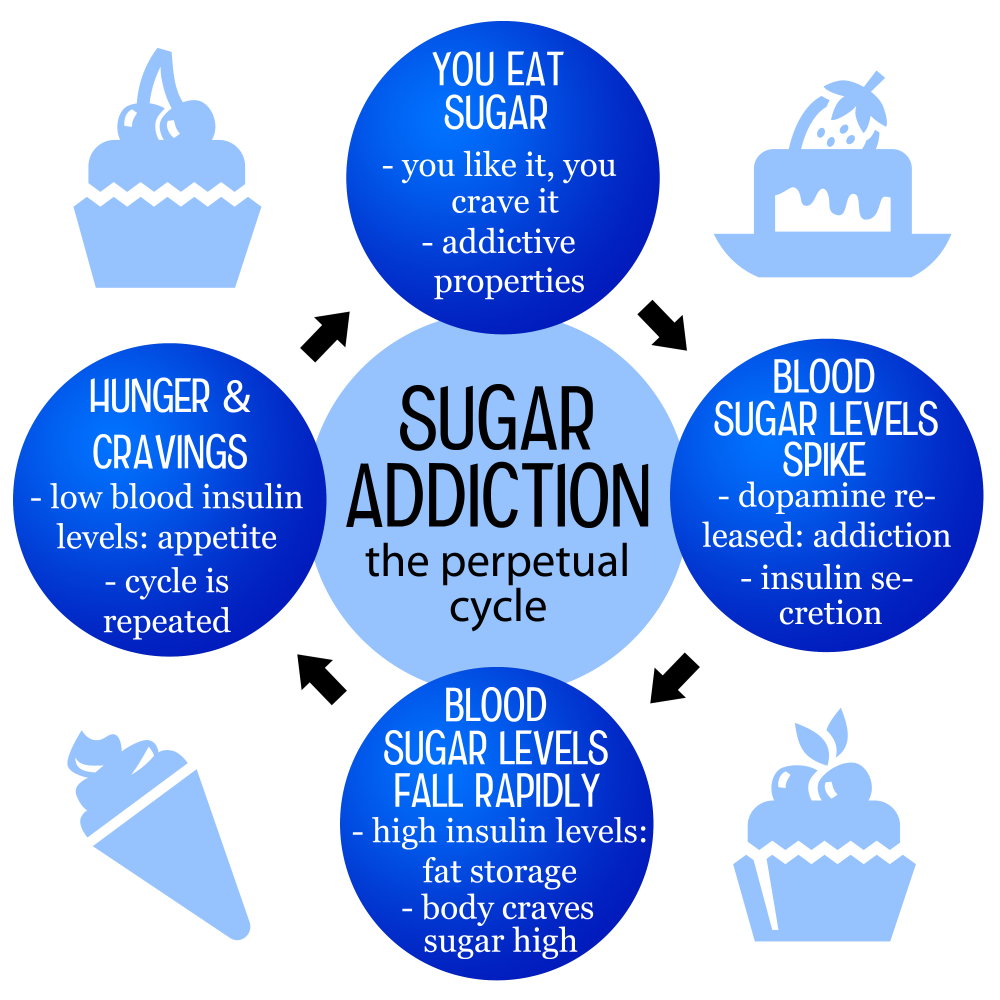
Sugar addiction is a hotly contested topic within the nutrition field. While substances like alcohol and nicotine are classified as addictive based on established clinical criteria, sugar’s classification remains less straightforward. Research shows sugar consumption elevates cravings and can lead to compulsive eating patterns, simulating addiction-like behavior. However, the American Psychological Association has not classified sugar as an addictive substance, leaving room for debate regarding its addictive properties.
The allure of sugar lies in its presence in ultra-processed foods that are abundantly available today. These foods often contain added sugars alongside unhealthy fats and sodium, making them highly palatable and easy to overconsume. When individuals decide to reduce or eliminate these sugary foods, they might experience withdrawal symptoms akin to those seen in substance addiction. This creates a complex relationship between craving for sugar and the health effects of excessive sugar consumption.
Health Effects of Sugar Consumption
The health effects of sugar consumption become more concerning when we examine the average intake rates. Current dietary data reveals that many individuals in the U.S. consume nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, which far exceeds the American Heart Association’s recommended limits. For men, the recommendation is no more than 9 teaspoons, while it is 6 teaspoons for women and even less for children. Excessive sugar intake is linked to various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease, reinforcing the need for mindful eating.
Furthermore, sugar consumption not only affects physical health but also has psychological repercussions. Habitual consumption of sugary foods can create a cycle of cravings that can lead to emotional eating or a decrease in overall well-being. When we consider added sugars in our diets, it becomes crucial to understand the implications they have on our health and to recognize the importance of moderation in our sugar intake.
The Science Behind Sugar Cravings
Cravings for sugar can occur due to both physiological and psychological factors. On a biological level, consuming sugar releases dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward in the brain. This release can create a feedback loop where individuals seek out sugary foods to induce feelings of happiness or satisfaction, leading to increased sugar consumption over time. It’s a complex interplay between our body and our desires, making it essential to understand why sugar can seem so addictive.
In addition to biological factors, habits and environmental cues play a significant role in triggering sugar cravings. For instance, many people unconsciously reach for sugary snacks during stressful situations or social gatherings, associating these moments with treats. This behavioral pattern reinforces the urge to consume more sugar, creating a cycle that can be hard to break. Recognizing these triggers is key to cultivating healthier eating habits and managing sugar cravings effectively.
Tips for Reducing Added Sugar Intake
Reducing added sugar intake is vital for both physical and mental health. One practical approach is to read food labels diligently. Many processed foods contain hidden sugars that contribute to overall consumption figures. By identifying these products and limiting their intake, individuals can significantly decrease their daily sugar count. Additionally, opting for whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can satisfy sweet cravings while providing essential nutrients without added sugars.
Another effective strategy is to gradually reduce sugar intake rather than going cold turkey. Abruptly cutting sugar can lead to intense cravings and withdrawal-like symptoms, making it harder to maintain changes. By slowly decreasing the amount of added sugar in meals, such as by using less sugar in coffee or choosing less sweet snacks, individuals can acclimate their taste buds and lessen their dependence on sugary foods over time.
The Role of Sugar in a Balanced Diet
Despite concerns surrounding sugar, it’s important to acknowledge that a certain level of sugar is necessary in our diets. Naturally occurring sugars found in fruits and dairy products provide our bodies with energy and essential nutrients. The key lies in balance; moderation is critical. While it’s possible to enjoy sweets and desserts, they should be consumed in conjunction with a variety of other nutrient-rich foods.
Balancing sugar intake also means understanding the difference between natural and added sugars. While natural sugars are part of a healthy diet, the issue primarily revolves around the overwhelming amounts of added sugars present in many processed foods. By focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and being aware of the added sugars in products, individuals can maintain a balanced diet that supports overall health and well-being.
Coping with Sugar Withdrawal Symptoms
When individuals attempt to reduce their sugar intake, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and mood swings. These symptoms can be daunting, often leading people to revert to their old sugar-consuming habits. Acknowledging these symptoms as a temporary part of the adjustment process is crucial; they reflect the body’s adaptation to lower sugar levels.
To ease the transition, it can be helpful to embrace healthier food substitutes that provide sweetness without excessive calories. Fruits, for example, can satisfy sweet cravings while delivering fiber and vitamins. Staying hydrated and ensuring adequate nutrition through balanced meals can also help mitigate withdrawal effects, allowing individuals to navigate their sugar reduction journey more smoothly.
Exploring Alternatives to Sugar
As we strive to lower our sugar intake, many people seek alternatives that can still satisfy their sweet tooth without the health risks associated with excessive sugar consumption. Natural sweeteners like honey, maple syrup, and stevia offer options that can be more beneficial when used in moderation. Additionally, these alternatives provide different flavor profiles that can enhance foods and beverages without relying solely on refined sugars.
Experimenting with spices such as cinnamon or vanilla can also help create a perception of sweetness in foods without adding sugar. By incorporating these alternatives and flavor enhancers, individuals can create satisfying meals and snacks that reduce cravings for sugary foods, supporting their goal of healthier eating without feeling deprived.
Understanding the Impact of Sugar on Mood
One of the lesser-known effects of sugar consumption is its impact on mood. The quick energy boost that comes from consuming sugar can lead to a temporary feeling of happiness or euphoria, which might create a cycle of dependency on sugary foods for emotional regulation. Over time, however, this can lead to mood swings, crashes in energy, and increased irritability as blood sugar levels fluctuate significantly after consuming high-sugar items.
Research suggests that regular high sugar intake can contribute to long-term mood disorders such as anxiety and depression. As the brain becomes accustomed to the high levels of sugar and the corresponding dopamine response, it may become less sensitive to these rewards, causing individuals to consume even more sugar in a quest for the same pleasurable effects. Understanding these dynamics is essential for anyone wanting to improve their mental well-being.
The Importance of Education on Sugar Consumption
Increased awareness and education about sugar consumption and its related health effects are essential for making informed dietary choices. Many people are unaware of the significant amounts of added sugar present in everyday foods and beverages. By providing resources and information on reading nutrition labels and understanding ingredients commonly associated with sugar, individuals can take proactive steps in managing their sugar intake.
Educational initiatives can empower consumers to make healthier choices by promoting awareness around the potential health consequences of excessive sugar consumption. Workshops, community programs, and online resources can help spread knowledge about the importance of a balanced diet, encouraging individuals to opt for healthier, less sweet alternatives while maintaining a diverse and enjoyable diet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive and how does sugar consumption affect cravings?
While sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, it can lead to cravings and compulsive eating. Many people experience withdrawal-like symptoms when reducing sugar intake, indicating that sugar can have addictive qualities. High sugar consumption from ultra-processed foods increases cravings due to their palatability.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Sugar addiction can lead to health issues such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Excessive added sugar consumption is linked to negative health consequences. Although not officially classified as addictive, the psychological effects of sugar addiction can manifest through strong cravings and habitual overeating.
Are there withdrawal symptoms associated with reducing added sugar intake?
Yes, when individuals cut back on added sugar, they may experience withdrawal symptoms like headaches, dizziness, and anxiety. These effects occur because high sugar diets can lead to compulsive eating behaviors, making it challenging to stop abruptly. Gradual reduction is often recommended.
How does added sugar contribute to sugar cravings?
Added sugar can increase cravings for sweets due to its highly palatable nature. Foods rich in added sugars are often more accessible and appealing, which leads to habitual consumption and subsequently stronger cravings for sugar, creating a cycle that can be hard to break.
What is the recommended daily limit for sugar consumption?
The American Heart Association recommends that men limit their intake to no more than 9 teaspoons and women to no more than 6 teaspoons of added sugar daily. This helps to maintain health and reduce the risk of sugar-related health issues.
Can consuming sugar in moderation have benefits?
Yes, consuming sugar in moderation can enhance flavor and pleasure in meals. It’s important to distinguish between necessary sugars found in fruits and whole foods and excessive added sugars that can lead to health issues. Balance is key in achieving a healthy diet.
How do ultra-processed foods relate to sugar addiction?
Ultra-processed foods often contain high levels of added sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium, which can foster cravings and increase consumption. These foods are designed to be extremely palatable, leading to habitual overeating and potentially contributing to sugar addiction.
Is it possible to replace sugar addiction with healthier alternatives?
Yes, transitioning away from added sugars can begin with gradual reductions and incorporating healthier alternatives such as fruits or naturally sweetened foods. This approach can help mitigate cravings for sugar while still satisfying the desire for sweetness.
What role does psychology play in sugar addiction?
Psychological factors play a significant role in sugar addiction, as cravings can be driven by emotional responses, stress, and reward mechanisms in the brain. Understanding these triggers can help individuals manage their sugar consumption more effectively.
Is sugar consumption the same for everyone?
No, sugar consumption varies by individual based on factors such as metabolism, lifestyle, and dietary habits. While some can manage moderate sugar intake, others may be more susceptible to cravings and negative health impacts due to higher consumption.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Is sugar addictive? | Sugar increases cravings and compulsive eating behaviors but is not classified as addictive like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Effects of sugar consumption | Withdrawal-like symptoms can occur when sugar is discontinued suddenly, such as headaches and anxiety, but they are less severe compared to addictions to drugs or alcohol. |
| Sugar in our diet | Sugar is found in many essential foods like fruits and whole grains, and moderate consumption is beneficial. |
| Current sugar consumption | Americans typically consume around 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, significantly above recommended levels. |
| Recommendations | The American Heart Association suggests no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women. |
| Eliminating sugar | Cold turkey cessation may be counterproductive; gradually reducing intake is advised. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This complex question continues to be debated among nutrition experts. While sugar can lead to cravings similar to addictive substances, it is not technically classified as addictive. Understanding sugar’s role in our diets is crucial; moderate consumption can be part of a healthy lifestyle. Importantly, awareness of sugar intake is key to maintaining health, as excessive added sugars can lead to significant health issues. Thus, careful management of sugar intake can help us enjoy its benefits without falling into unhealthy habits.