Maternal mortality in the U.S. continues to rise, revealing a troubling trend in a nation that leads high-income countries in pregnancy-related deaths. Despite more than 80% of these deaths being preventable, systemic issues such as maternal health disparities, inadequate postpartum care, and chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease contribute to an alarming mortality rate. Between 2018 and 2022, the U.S. saw significant increases in maternal deaths, particularly affecting marginalized racial groups. American Indian and Alaska Native women experienced the steepest rates, highlighting deeply entrenched inequities in maternal health. Addressing these preventable deaths requires urgent attention to enhance prenatal care and postpartum support, as the health of mothers directly impacts the wellbeing of future generations.
The alarming rise in maternal fatalities during childbirth in the United States, often identified as pregnancy-related deaths, underscores a critical public health crisis. This situation highlights the alarming needs for improved maternal wellness initiatives, particularly regarding health equity and accessibility to comprehensive postpartum care. Chronic issues like cardiovascular diseases are now recognized as increasingly significant risk factors, which complicate pregnancy and childbirth significantly for many women. Furthermore, systemic failures in healthcare provision have led to stark disparities, especially among different racial and ethnic groups. As we delve into this pressing issue, it becomes crucial to explore innovative strategies aimed at reducing these preventable losses and fostering an environment where maternal health is prioritized.
The Current State of Maternal Mortality in the U.S.
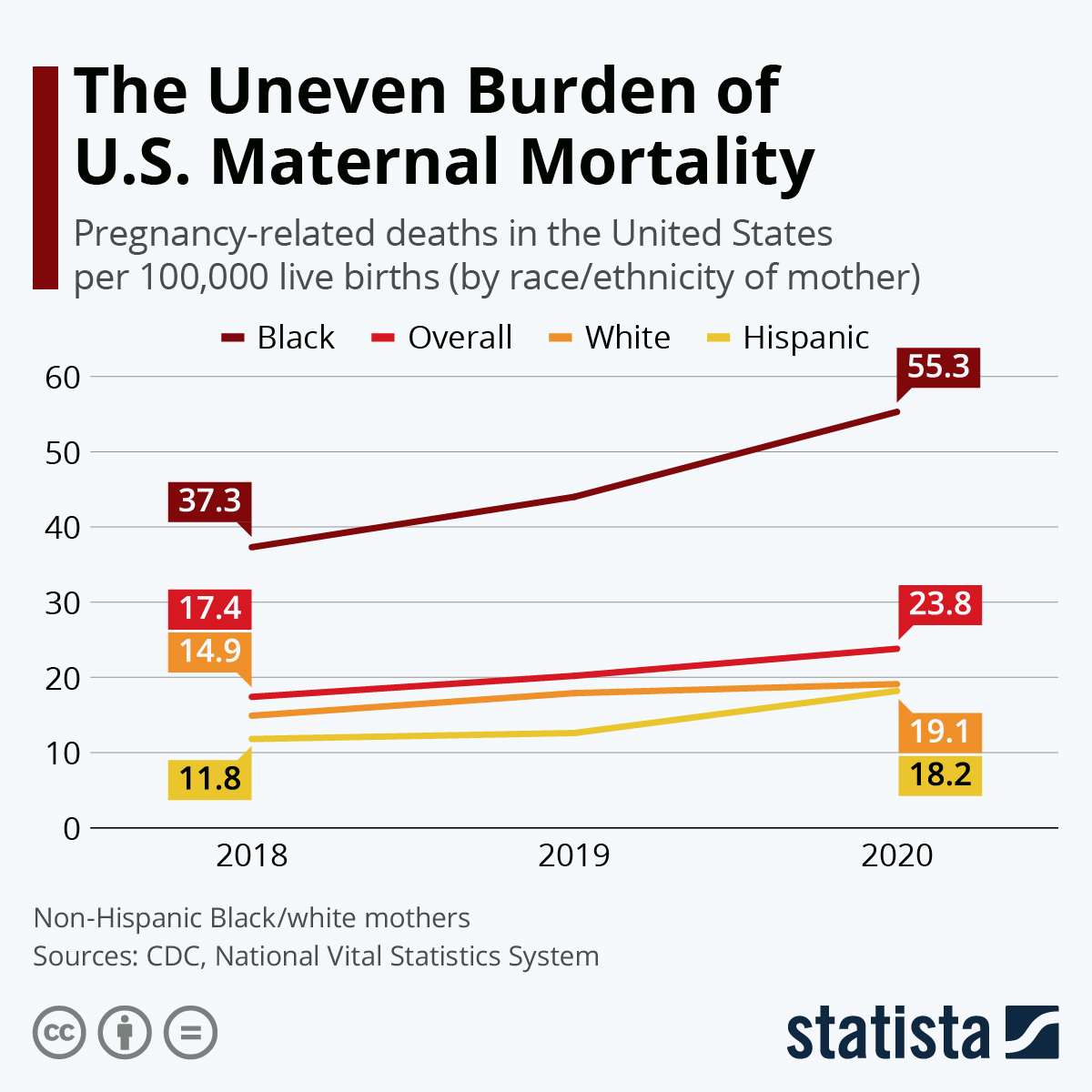
In recent years, the United States has grappled with an alarming rise in maternal mortality rates, making it the leader in maternal deaths among high-income countries. A pivotal study has revealed that over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, yet the statistics tell a grim story: between 2018 and 2022, the rate of maternal mortality escalated, particularly spiking during the COVID-19 pandemic. The latest data reveals a significant increase, with 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births recorded in 2022, compared to 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018. Factors contributing to this rise include an increasingly complex healthcare system plagued by inequities and the high prevalence of chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease among women of reproductive age.
Moreover, the disparities presented in the findings are striking, as maternal mortality rates vary dramatically across racial and ethnic lines. American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest mortality rate, nearly four times that of white women, underscoring the urgent need for a multi-faceted approach to address these disparities. The continuum of care must expand beyond initial pregnancy care to include comprehensive postpartum support, as a substantial number of maternal deaths occur after the traditional postpartum period within the first year following childbirth. This reality highlights that the structure of maternal healthcare in the U.S. requires urgent reform.
Understanding Maternal Health Disparities
Maternal health disparities represent a pressing challenge within the American healthcare landscape, where systemic inequalities perpetuate significantly higher rates of mortality among certain demographics. The study highlights that Black and Native American women, in particular, experience alarmingly high rates of pregnancy-related deaths, attributed not only to socio-economic factors but also to biases entrenched in healthcare systems. These disparities call for an urgent reevaluation of healthcare policies to address the root causes of inequity, focusing on providing equitable access to quality maternal care, especially in underserved areas.
Addressing these disparities requires not only targeted interventions and policy changes but also a robust commitment to improving healthcare education and awareness in communities. Programs aimed at reducing maternal health disparities must prioritize prenatal care access, as well as education on recognizing and managing chronic conditions that threaten maternal health. Collaborative efforts among healthcare providers, community organizations, and policymakers are essential to eliminate these gaps, ensuring that every woman has access to the comprehensive care she needs throughout her maternity journey.
The Role of Cardiovascular Disease in Pregnancy-Related Deaths
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., with over 20% of maternal deaths attributed to various cardiovascular disorders such as hypertension, pre-eclampsia, and cardiac complications. This shift in maternal mortality causes reflects the changing health profiles of women entering pregnancy, who are increasingly affected by chronic conditions at younger ages. As health issues like hypertension are becoming common among younger women, there’s an urgent need for healthcare systems to adapt and implement preventative measures, monitoring, and comprehensive management of cardiovascular health prior to and during pregnancy.
Furthermore, understanding the correlation between cardiovascular disease and maternal mortality necessitates improved prenatal screening and ongoing care. Clinicians must prioritize early detection and intervention strategies for women at risk of hypertension and related complications. By integrating cardiovascular health management into the prenatal care paradigm, we can significantly reduce the incidence of preventable maternal deaths caused by cardiovascular issues, ensuring healthier outcomes for both mothers and their children.
Importance of Postpartum Care for Maternal Health
Postpartum care is crucial for safeguarding maternal health, yet it often receives inadequate attention within the healthcare framework. The period following childbirth is not just a brief window; evidence shows that nearly one-third of pregnancy-related deaths occur after the initial 42 days postpartum. This highlights the necessity of rethinking the traditional timelines of postpartum care, which often conclude too early to effectively monitor and address potential health complications. To enhance maternal health outcomes, extending postpartum care to cover the entire first year after childbirth is essential.
Comprehensive postpartum care should encompass continuous health assessments, mental health support, and lifestyle guidance to ensure women recover fully from childbirth. Addressing both physical and emotional health challenges during this time can prevent the escalation of issues that might lead to severe health consequences, including maternal death. Establishing a structured system that prioritizes postpartum visits and resources can vastly improve the overall health trajectory for mothers, aiding in their recovery and well-being.
Prevention of Preventable Maternal Deaths
Addressing the high rates of preventable maternal deaths requires a multifaceted approach, particularly as the data shows that the vast majority of these deaths could have been avoided. Effective prevention strategies must include enhanced access to quality maternity care, streamlined care coordination, and improved public health initiatives focused on maternal health. The U.S. must prioritize investments in maternal health systems that address these critical issues head-on, working to establish a standard of care accessible to all pregnant individuals, regardless of their socio-economic or geographical barriers.
Moreover, successful prevention of these deaths hinges upon community-level interventions that empower women with knowledge about their health, preventive care options, and early warning signs of complications during pregnancy and postpartum. Healthcare providers, together with community organizations, must encourage educational outreach that equips women with the information necessary to advocate for their health. By fostering a supportive environment that prioritizes maternal health, we can significantly reduce the occurrence of preventable maternal deaths.
Learning from California’s Maternal Health Success
California serves as a model for improving maternal health outcomes, showcasing that targeted strategies can significantly lower the state’s pregnancy-related death rates. With a concerted effort to address maternal health disparities and enhance the overall level of care, California has managed to reduce its maternal mortality rates through comprehensive policy implementation and innovative health programs. Identifying successful strategies employed in California is critical for other states struggling with higher maternal mortality rates, as they indicate that improvements are possible.
Key strategies such as fostering collaboration between healthcare providers, increasing funding for maternal health initiatives, and implementing statewide maternal mortality review committees can lead to more informed policymaking. Furthermore, scaling up successful community-based programs that prioritize prenatal and postpartum care can empower more states to follow California’s example and make strides in reducing pregnancy-related deaths while improving health equity across the nation.
The Impact of Healthcare System Variability
Variability in healthcare systems across the U.S. has a profound impact on maternal health outcomes. The differences in quality and accessibility of prenatal and postpartum care services contribute heavily to the varying rates of pregnancy-related deaths between states. This patchwork nature of healthcare means that while some states achieve lower mortality rates through effective policies and practices, others fall behind, exacerbating maternal health disparities. Addressing this variability is crucial for achieving more equitable maternal care across the country.
Emphasizing the need for uniform standards of care and cohesive policies can pave the way for improvements in maternal health. National guidelines that mandate comprehensive maternity care and postpartum support could help mitigate the inconsistent quality of care women receive based on their location or demographic background. By promoting a more cohesive approach to maternal health, we can better safeguard mothers and ensure that all women receive the quality care they deserve during and after pregnancy.
The Role of Research in Improving Maternal Health
Investing in maternal health research is paramount for understanding the challenges and barriers contributing to high maternal mortality rates. Comprehensive data collection and analysis are vital for identifying trends and disparities within maternal health, allowing for informed policy decisions and targeted interventions. Researchers play a crucial role in shedding light on the systemic issues that contribute to maternal mortality, providing the evidence needed to advocate for change and promote best practices in maternal healthcare.
Furthermore, enhancing funding for maternal health research can empower innovations aimed at addressing maternal mortality. Encouraging collaboration across academic institutions, public health officials, and community stakeholders can foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement within maternal health systems. As we invest in research-focused initiatives, we enable healthcare systems to adapt and evolve, ultimately paving the way for decreased maternal fatalities and improved outcomes for mothers and their infants.
Advocating for Maternal Health Policies
Advocacy plays a crucial role in driving policy change related to maternal health. As the statistics around maternal mortality continue to reveal systemic issues, it becomes imperative for stakeholders, including healthcare providers, community leaders, and policymakers, to collaborate and push for evidence-based reforms. Effective advocacy can help highlight the importance of addressing disparities and improving access to care, ensuring that the maternal health crisis receives the attention it deserves on both state and federal levels.
Moreover, mobilizing communities to advocate for their maternal health needs is essential for creating lasting change. Grassroots movements can bring awareness to local and national issues, highlighting the voices and experiences of women affected by maternal health disparities. By fostering a culture of advocacy, communities can work together to demand improvements in care, funding for maternal health initiatives, and policies that align with the goal of reducing preventable maternal deaths, ultimately forging a more equitable future for all women.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Maternal mortality in the U.S. is primarily driven by cardiovascular disease, which accounts for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths. Other significant factors include postpartum complications, hemorrhage, and conditions exacerbated by chronic health issues such as hypertension.
How does the U.S. maternal mortality rate compare to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with persistent disparities in rates across different racial and ethnic groups. Factors contributing to this include a fragmented healthcare system and inequitable access to prenatal and postpartum care.
What role do maternal health disparities play in pregnancy-related deaths?
Maternal health disparities significantly affect pregnancy-related deaths, with racial and ethnic minorities experiencing disproportionately higher mortality rates. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face mortality rates nearly four times higher than white women.
How can improve postpartum care reduce maternal mortality rates?
Improving postpartum care is essential as late maternal deaths, occurring up to a year after pregnancy, account for nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths. Enhancing healthcare access and support during this period can significantly lower these mortality rates.
Which states have the highest rates of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
In the U.S., maternal mortality rates vary greatly by state, with some states having rates as low as 18.5 deaths per 100,000 live births and others as high as 59.7. Addressing these variations requires targeted policies and interventions to improve maternal health outcomes.
How does cardiovascular disease relate to maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of maternal mortality in the U.S., increasingly affecting younger individuals due to rising rates of chronic health issues like hypertension. This shift underscores the need for better management of cardiovascular health during pregnancy.
What can be done to prevent pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
To prevent pregnancy-related deaths, there must be a strong focus on improving healthcare infrastructure, enhancing access to prenatal and postpartum care, and implementing innovative policies that address maternal health disparities across different demographics.
Why should we consider late maternal deaths in discussions about maternal mortality?
Late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and 1 year after pregnancy, are critical to addressing maternal mortality. Recognizing this timeframe highlights the need for ongoing healthcare during the postpartum period, challenging the traditional six-week recovery model.
What impact has COVID-19 had on maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
The COVID-19 pandemic has likely exacerbated the rise in maternal mortality rates, particularly in 2021. The disruptions in healthcare access and increased stressors during the pandemic have intensified existing maternal health disparities.
What policies are needed to address maternal health disparities in the U.S.?
Effective policies to mitigate maternal health disparities must include increased funding for maternal health programs, improved data tracking systems, and initiatives aimed at reducing inequities in healthcare access across different states and communities.
| Key Statistics | Disparities | Causes of Death | Policy Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 rate: 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births (up from 25.3 in 2018) | American Indian/Alaska Native: 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births (highest) | Main cause: Cardiovascular disease (20% of deaths) | Invest in public health infrastructure and maternal care support |
| Highest increase observed in 2021, likely due to COVID-19 | Non-Hispanic Black: 76.9 deaths per 100,000 live births | Shift from hemorrhage to cardiovascular disease as leading cause | Address state-level disparities and equitable healthcare access |
| Pregnancy-related deaths rose in all age groups tested from 2018-2022 | White: 27.6 deaths per 100,000 live births | Increase in hypertension cases among younger populations | Implement comprehensive postpartum care beyond the 6-week mark |
Summary
Maternal mortality in the U.S. remains a critical issue, as recent data shows an alarming rise in pregnancy-related deaths over the past few years. Despite the potential for many of these deaths to be preventable, the U.S. has consistently recorded the highest maternal mortality rates among high-income nations. The findings call for urgent action to address systemic healthcare disparities, improve prenatal care, and ensure comprehensive postpartum support. Investments in public health infrastructure and targeted policy changes are essential to reverse this trend and safeguard the health of mothers across the country.